Nonlinear dynamics of continuous media
Research directions:
Investigation of the dynamics of systems with time-varying stiffness and mass parameters.
Dynamics of elastic structures interacting with moving ice cover.
Detachment of the film from the substrate under external impact.
Main results:
The process of damage growth in the film substrate under impact and stationary impacts has been studied. The possibility of damage growth because of the process of wave localization in the area with initial damage is shown, and a program for calculating the behavior of the film depending on the type of impact is compiled.
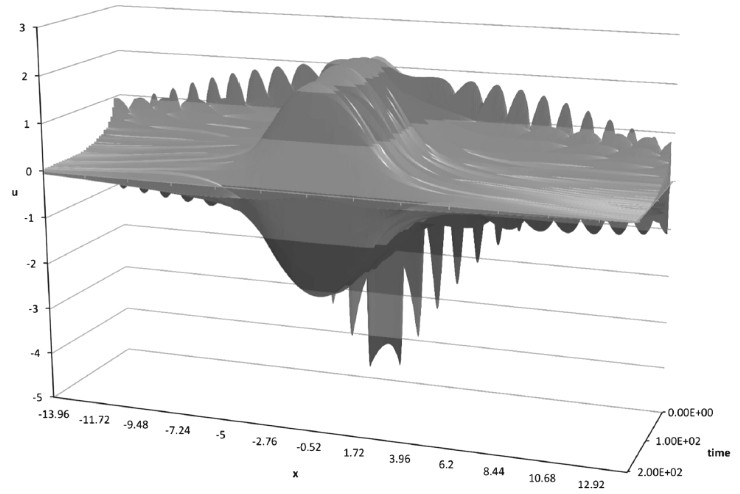
The dependence of the film displacement under impact.
Analytical methods are proposed for studying the dynamics of weakly nonlinear elastic beams with time-varying mass, or mass and stiffness (including that which changes as a result of material aging). A criterion has been developed for how, when applying methods of the Galerkin type, it is necessary to choose the number of modes taken into account in the solution of the problem being constructed. The results obtained are applied to the study of the phenomenon of vibration caused by rain and wind.
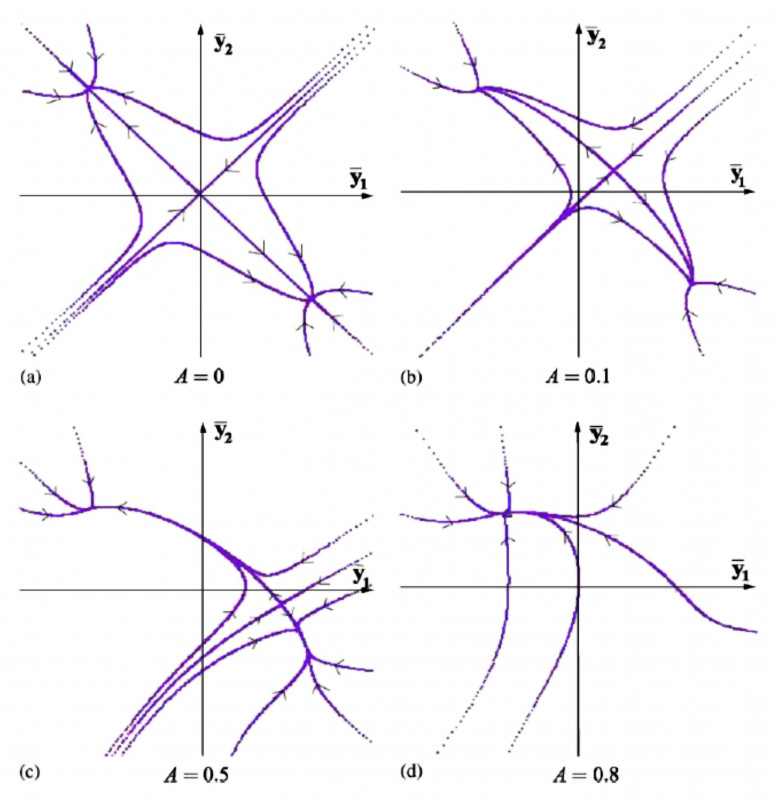
Phase portraits of the oscillator when changing the position of the variable rain mass located on the surface of the suspension bridge cable.
A continuum model has been proposed to describe ice-induced vibrations for offshore structures anchored to the bottom (such as oil platforms, wind turbines, for example).
Methods and programs have been developed to describe the dynamics of offshore structures interacting with a moving ice cover based on a simple mechanical model. The main modes of vibration are described, including the most dangerous ones in terms of strength. A model is proposed that describes the presence of water and broken ice in the gap between the structure and the ice cover. Wave regimes in liquid and ice cover are also considered during the operation of mechanisms on a floating structure, taking into account the gap between the structure and ice.